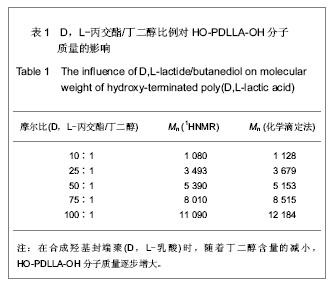
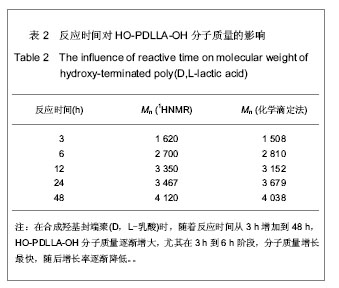
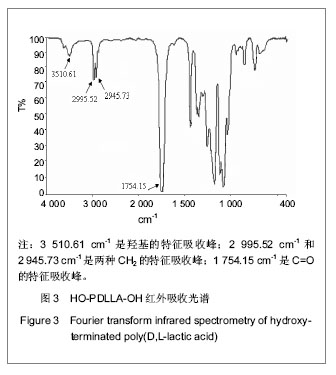
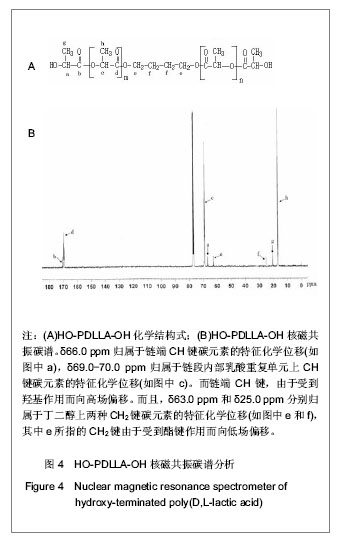
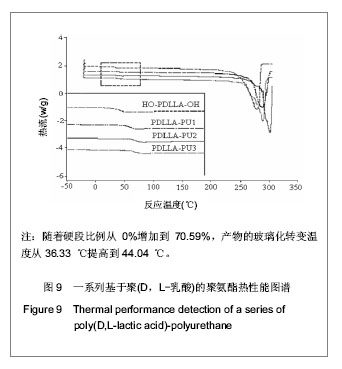
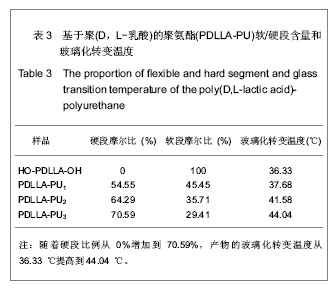
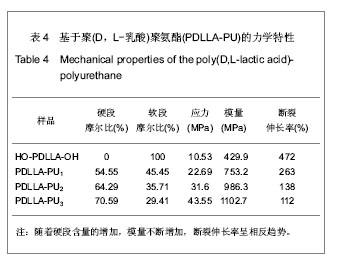
| [1] Merline JD, Nair CPR, Gouri C, et al. Polyether polyurethanes: synthesis, characterization, and thermoresponsive shape memory properties. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;107(6): 4082-4092.[2] Wang N, Dong A, Radosz M, et al. Thermoresponsive degradable poly(ethylene glycol) analogues. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2008;84(1):148-157.[3] Huang X, Nayak BR, Lowei TL. Synthesis and characterization of novel thermoresponsive-co-biodegradable hydrogels composed of N-isopropylacrylamide, poly(L-lactic acid), and dextran. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem. 2004; 42(20):5054-5066.[4] Zhan JJ, Chen CH, Pan Y. Gaofenzi Tongbao. 2006;(8):21-28.湛建阶,陈朝辉,盘毅.形状记忆聚氨酯研究进展[J].高分子通报, 2006,(8):21-28.[5] Chen G, Imanishi YK, Ito Y. Effect of protein and cell behavior on pattern-grafted thermoresponsive polymer. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998;42(1):38-44.[6] Kaursoin J, Agrawal AK. Melt Spun Thermoresponsive shape memory fibers based on polyurethanes: effect of drawing and heat-setting on fiber morphology and properties. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;103(4):2172-2182.[7] Watanabe E, Tomoshige N, Uyama H. New biodegradable and thermoresponsive polymers based on amphiphilic poly(asparagine) derivatives. Macromol Symp. 2007; 249-250(1):509-514.[8] Bian J, Lin HL , He FX , et al. Fabrication of microwave exfoliated graphite oxide reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites: Effects of filler on morphology, mechanical, thermal and conductive properties. Compos Part A-Appl S. 2013;47:72-82.[9] Sonnenschein MF , Ginzburg VV , Schiller KS, et al. Design, polymerization, and properties of high performance thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers from seed-oil derived soft segments. Polymer. 2013;54(4):1350-1360.[10] Liu C, Qin H, Mather PT. Review of progress in shape- memory polymers. J Mater Chem. 2007;17(16): 1543-1558. [11] Baer G., Wilson TS, Matthews DL, et al. Shape-memory behavior of thermally stimulated polyurethane for medical applications. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;103(6):3882-3892.[12] Ni QQ, Zhang CS, Fu YQ, et al. Shape memory effect and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Compos Struct. 2007;81(2): 176-184.[13] da Silva RM, Mano JF, Reis RL. Smart thermoresponsive coatings and surfaces for tissue engineering: switching cell-material boundaries. Trends Biotechnol. 2007;25(12): 577-583.[14] Jiang XW, Xiong DA, An YL, et al. Thermoresponsive hydrogel of poly(glycidyl methacrylate-co-N- isopropylacrylamide) as a nanoreactor of gold nanoparticles. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem. 2007;45(13):2812-2819.[15] Ajili SH, Ebrahimi NG, Soleimani M. Polyurethane/ polycaprolactane blend with shape memory effect as a proposed material for cardiovascular implants. Acta Biomaterialia. 2009;5(5):1519-1530.[16] Mehdi B, Khalid MZ, Ijaz AB, et al. Molecular engineering and properties of chitin based shape memory polyurethanes. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2008;74(3):621-626.[17] Gao LJ, Zhou LM , Fang SM , et al. New copoly(urethane-methacrylate)s obtained by adjusting the content of the poly(1,2-propanediol ortho-phthalate): Transparent, thermal, and mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci. 2013;128(6):3900-3905.[18] Saha S, Saha U, Singh JP, et al. Thermal and mechanical properties of homogeneous ternary nanocomposites of regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene)-wrapped multiwalled carbon nanotube dispersed in thermoplastic polyurethane: Dynamic- and thermomechanical analysis. J Appl Polym Sci. 2013;128(3):2109-2120.[19] Heuchel M, Sauter T, Kratz K, et al. Thermally induced shape-memory effects in polymers: Quantification and related modeling approaches. J Polym Sci Pol Phys. 2013;51(8): 621-637.[20] Lendlein A, Zotzmann J, Feng Y, et al. Controlling the switching temperature of biodegradable, amorphous, shape-memory poly(rac-lactide)urethane networks by incorporation of different comonomers. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(4):975-982.[21] Nagahama K, Ueda Y, Ouchi T, et al. Biodegradable shape-memory polymers exhibiting sharp thermal transitions and controlled drug release. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(7): 1789-1794.[22] Behl M, Ridder U, Feng YK, et al. Shape-memory capability of binary multiblock copolymer blends with hard and switching domains provided by different components. Soft Matter. 2009; 5(3):676-684.[23] Zhang W, Chen L, Zhang Y. Surprising shape-memory effect of polylactide resulted from toughening by polyamide elastomer. Polymer. 2009;50(5):1311-1315.[24] Wong YS, Xiong Y, Venkatraman SS, et al. Shape memory in un-cross-linked biodegradable. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008; 19(2):175-191.[25] Wang YL, Ruan CS, Sun JX, et al. Degradation studies on segmented polyurethanes prepared with poly(D,L-lactic acid) diol, hexamethylene diisocyanate and different chain extenders. Polym Degrad Stabil. 2011;96(9):1687-1694.[26] Ruan CS, Wang YL, Zhang, ML , et al. Design, synthesis and characterization of novel biodegradable shape memory polymers based on poly(D,L-lactic acid) diol, hexamethylene diisocyanate and piperazine. Polym Inter. 2012;61(4): 524-530.[27] Kim HI, Ishihara K, Lee S, et al. Tissue response to poly(D,L-lactic acid)-based blend with phospholipid polymer for biodegradable cardiovascular stents. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(9):2241-2247. [28] Feng YK, Behl M, Kelch S, et al. Biodegradable multiblock copolymers based on oligodepsipeptides with shape-memory properties. Macromol Biosci. 2009;9(1):45-54. |
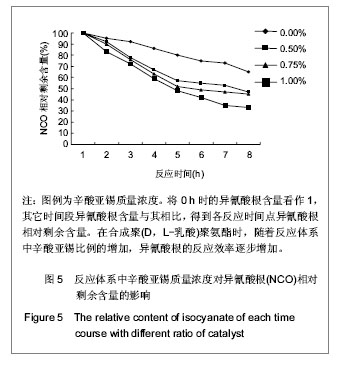
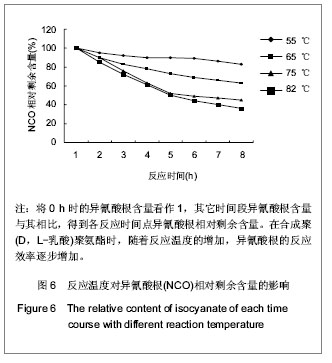
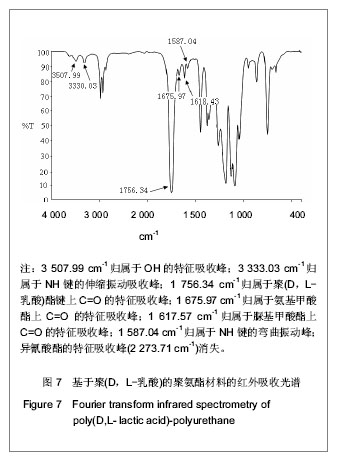
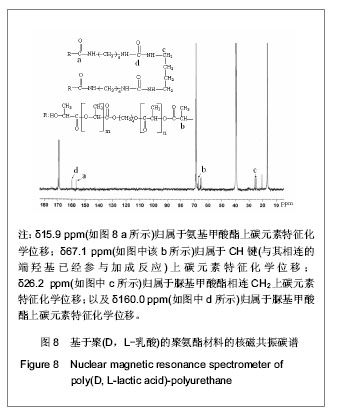
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)